February 17, 2025
As the demand for more sustainable energy solutions continues to grow, biodiesel and renewable diesel have emerged as key alternatives to traditional petroleum fuels. These renewable fuels offer environmental and economic benefits while helping to support energy independence and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. But what exactly are biodiesel and renewable diesel, and how are they being used today? Let’s explore the basics.
What is Biodiesel?
Biodiesel is a renewable fuel made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease. It is produced through a chemical process called transesterification, which converts these oils and fats into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME)—the chemical compound that makes up biodiesel. Biodiesel can be blended with petroleum diesel in various proportions, commonly referred to as B5 (5% biodiesel), B20 (20% biodiesel), or even B100 (100% biodiesel). It is biodegradable, non-toxic, and reduces harmful emissions compared to conventional diesel.
Emissions Reductions from Biodiesel
One of the most significant advantages of biodiesel is its ability to cut down on harmful emissions. The chart below illustrates how biodiesel compares to petroleum diesel in reducing key pollutants:
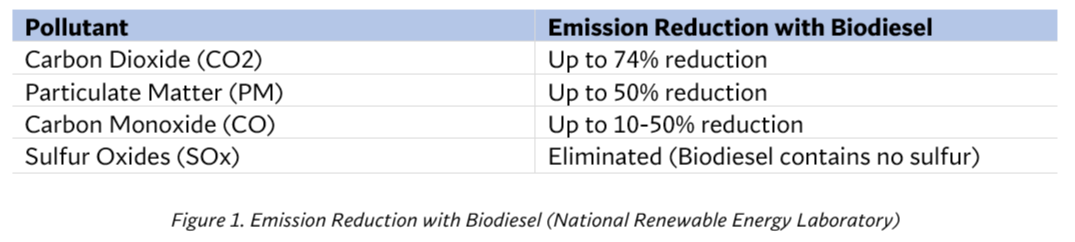
By utilizing renewable organic materials, biofuels can substantially lower the energy efficiency metrics of the transportation sector, contributing significantly to infrastructure sustainability, weatherization, and resilience. Strategically, biofuels offer several benefits, including enhanced energy security and economic opportunities. By diversifying the sources of transportation fuels and reducing reliance on imported oil, the U.S. can strengthen its energy independence and resilience to supply disruptions and price fluctuations in the global oil market.
What is Renewable Diesel?
Renewable diesel, also know as R-99, while also derived from organic sources, is different from biodiesel in its production process and chemical composition. Unlike biodiesel, which must be blended with petroleum diesel for optimal performance, renewable diesel is chemically similar to conventional diesel and can be used as a direct replacement without modification to engines or infrastructure – a drop-in fuel. It is produced through hydrotreating, a process that removes oxygen from the feedstock and creates a fuel that burns cleaner and more efficiently than petroleum diesel.
Benefits of Biodiesel and Renewable Diesel
Both biodiesel and renewable diesel offer a range of benefits, making them attractive options for various industries and fleets:
- Environmental Benefits: These fuels significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particulate matter, and other pollutants when compared to petroleum diesel.
- Energy Security: By utilizing domestic feedstocks such as soybean oil, waste fats, and algae, biodiesel and renewable diesel decrease dependence on imported fossil fuels.
- Engine Performance & Maintenance: Biodiesel has excellent lubricating properties compared to petroleum diesel which can reduce engine wear and tear. This can extend the life of fuel injectors, pumps, and other components. Renewable diesel, with its higher cetane rating, provides improved combustion efficiency and lower emissions.
Economic Opportunities: The production and use of these fuels create jobs in agriculture, refining, and distribution, supporting local and national economies.
How to Make the Switch: What You Need to Know
If you are considering switching to biodiesel or renewable diesel, here are key factors to keep in mind:
- Fuel Availability: Biodiesel is widely available at fueling stations across the U.S., often as a blend with petroleum diesel. Renewable diesel is more commonly found in states like California and Oregon and is now available on the East Coast. The Department of Energy’s Alternative Fuels Data Center provides an alternative fueling station locater to help you find the nearest available stations.
- Engine Compatibility: Biodiesel blends up to B20 can be used in most modern diesel engines without modifications. Higher blends, such as B100, may require engine modifications. Renewable diesel, on the other hand, is fully compatible with all diesel engines without any modifications.
- Cold Weather Considerations: Biodiesel has a higher cloud point than petroleum diesel, meaning it can gel in colder temperatures. In winter, lower biodiesel blends (B5 or B20) are recommended, and cold flow additives can help improve performance.
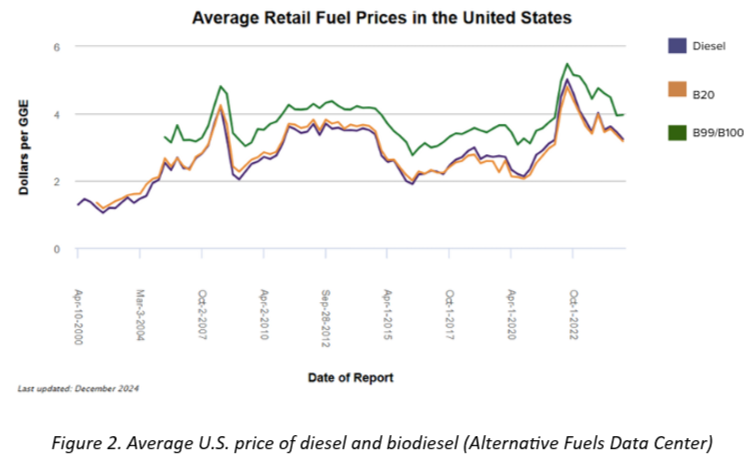
- Price Considerations: The price of biodiesel fluctuates based on the blend level and location. B20 (20% biodiesel and 80% conventional diesel) tends to be slightly more affordable than regular diesel, while higher blends, such as B99-B100, are typically more expensive. Diesel, due to its more complex processing, may also carry a higher price tag. However, the competitive growth of renewable diesel, incentives and reduced maintenance costs can help offset these higher expenses. As of October 2024, national average prices reported show biodiesel (B20) at $3.53 per gallon, biodiesel (B99-B100) at $4.04 per gallon, and conventional diesel at $3.64 per gallon (Alternative Fuels Data Center, December 2024). While higher biodiesel blends may have a steeper upfront cost, their positive impact on engine health and lower long-term maintenance expenses often make them a more economical choice in the long run.
Who Uses Biodiesel and Renewable Diesel?
Biodiesel and renewable diesel are widely used in various sectors, including:
- Transportation: Many commercial trucking companies and local governments use biodiesel blends to reduce fuel costs and emissions.
- Agriculture: Farmers utilize biodiesel in tractors and equipment to support sustainability efforts and improve air quality.
- Public Transit: City bus fleets incorporate these fuels to lower their carbon footprint.
Government Fleets: Municipalities, state agencies, and federal departments use biodiesel and renewable diesel to meet sustainability goals and comply with clean energy policies.
Industry Growth and Popularity
The demand for both biodiesel and renewable diesel is growing at an accelerated pace. Biodiesel production in the U.S. increased by nearly 10% from 2020 to 2023, and the industry is expected to continue growing as companies adopt more sustainable practices. Renewable diesel is gaining traction due to its compatibility with existing infrastructure and its cleaner combustion profile. In fact, renewable diesel production capacity is expected to double by 2026, driven by investments from major oil companies and refiners. As of 2024, global biodiesel production reached over 35 billion gallons, with the U.S. contributing around 15 billion gallons to the total output (U.S. Energy Information Administration). These growth figures demonstrate a clear shift towards energy affordability and reliability as governments and businesses set stricter emission reduction goals.
The Future of Biodiesel & Renewable Diesel
As technology and production processes improve, the adoption of biodiesel and renewable diesel is expected to grow. Biodiesel and renewable diesel present practical, scalable solutions for reducing emissions and enhancing energy security. As more industries and governments transition to fuel-independent energy solutions, these fuels will play an essential role in shaping a stronger transportation sector. Whether you’re a business owner, fleet manager, or sustainability advocate, exploring biodiesel and renewable diesel can be a meaningful step toward a greener future.
